Maximize Efficiencies With Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) Software
- A leading plastics global plastics manufacturer has standardized on Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) as one of their primary metrics based on its proven value in stabilizing every production machine on their shop floor.
- An injection molding manufacturer was able to increase OEE performance by 7% in three months, increasing gross profit by $1.2M across six production plants globally.
- Attaining an OEE score in the 80 to 85% range is widely considered to reflect a world-class manufacturing operation, according to Gartner.
- OEE is calculated by multiplying the (%) of time manufacturing machinery is available by production performance (ideal cycle time x total count/runtime and product quality (Good Count/Total Count).
Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) continues to gain in popularity as manufacturers seek to quantify plant, manufacturing line, and machine-level performance. Lean manufacturing and total productive maintenance (TPM) are the foundations of OEE. By providing valuable data to manufacturers at the machine level, Overall Equipment Effectiveness helps to find those factors that are deterministic, or that can be changed to further improve manufacturing performance over time.
Why Learning How To Maximize Efficiencies With OEE Matters
The majority of manufacturers begin using OEE to quantify the baseline performance for specific machinery and production assets. Taking this baseline-driven approach at the machine level enables manufacturers to scale the OEE metric across manufacturing units and production lines.
Combining OEE with additional manufacturing metrics helps manufacturers find random versus deterministic factors that have the greatest impact on production consistency and Quality. OEE is gaining adoption in process-related industries the fastest, including food & beverage, plastics, and oil & gas. Process-oriented machinery is prone to wide variations in consistency, quality, and throughput. OEE helps decipher the massive amount of data these machines produce, helping to find the main sources of variation. Knowing the sources of variation in process manufacturing workflows simplifies the complex interactions of machinery, substrates, materials, and environmental conditions that together act as constraints on production throughput and quality.
How To Calculate Overall Equipment Effectiveness
OEE is calculated by multiplying Machine Availability by Performance by Quality. Starting with Availability, Unplanned Downtime (UDT) and Planned Downtime (PDT) are subtracted from the total potential production time of the machine, asset, or entire production line. Unplanned downtimes (UDT) and planned downtimes (PDT) are subtracted from the total potential production time to provide the Run Time Availability is then calculated by dividing Run Time by Planned Production Time.
OEE’s Performance component is defined as the difference between the theoretical maximum output a given machine is capable of compared with actual output. Actual output is derived by subtracting out minor stoppages, reduced speed, and any other factor that reduces the performance levels of a given machine or asset. Performance is defined as the Ideal Cycle Time multiplied by the Total Count divided by the Run Time. Performance is also defined as the Total Production Count divided by the Run Time, divided by the ideal Run Rate.
The diagram below illustrates a use case for OEE. Having a true measure of machine availability, including Unplanned Downtime (UDT) and Planned Downtime (PDT), finds early signals of equipment malfunction, averting costly shutdowns.
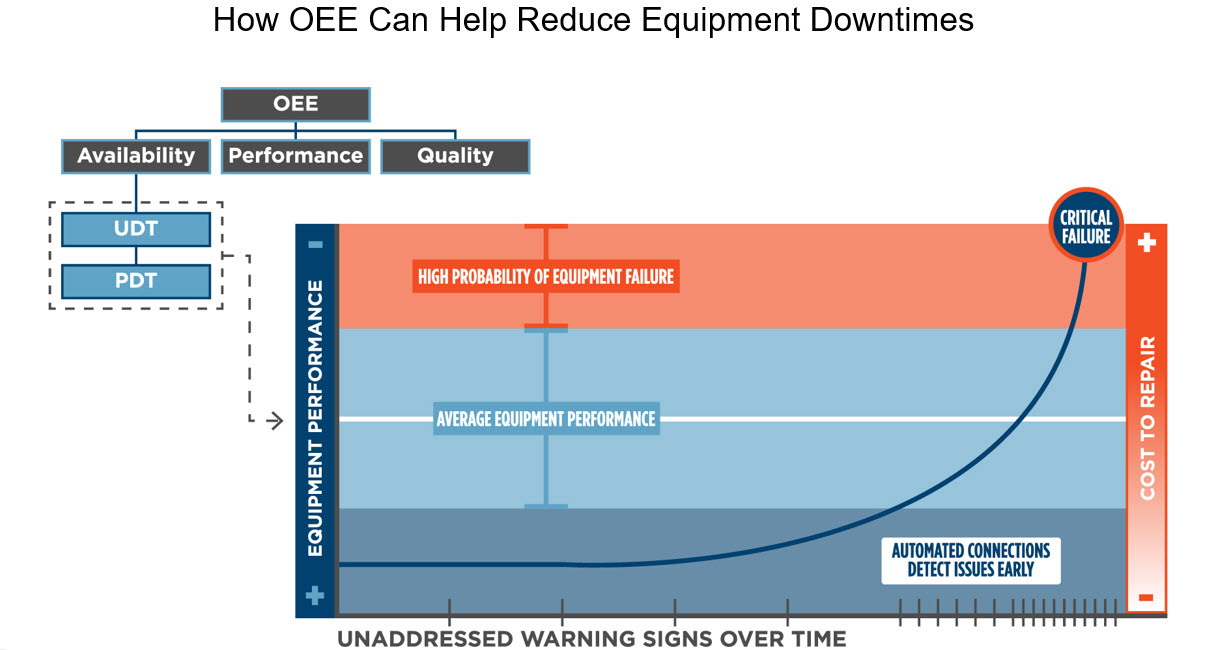
Quantifying quality is a valuable component of any OEE measurement. In discrete manufacturing operations, OEE quality resembles First Pass Yield. Like yield metrics, OEE quality measures the number of good parts that are successfully produced in a specific timeframe. Quality is calculated by taking the good product count divided by the total product count produced.
Conclusion
Benchmarking individual machine performance using OEE helps to gain new insights into potential new ways to increase yield rates, quality, and the useful life of a given machine. Stabilizing machinery performance is the factor that drives the majority of manufacturers first to adopt OEE.
For all of its contributions to improving manufacturing performance, it’s not meant to be used as a single, end-all metric of manufacturing performance. Instead, it’s best to group OEE into a dashboard of metrics that expand on visibility across all factors that can potentially influence the production yields, reliability and quality over time. OEE has the potential to revolutionize production operations taken in the context of overall manufacturing performance.




